- Home
- What is HMPV? Signs, Prevention, and Natural Treatments Explained
What is HMPV? Signs, Prevention, and Natural Treatments Explained
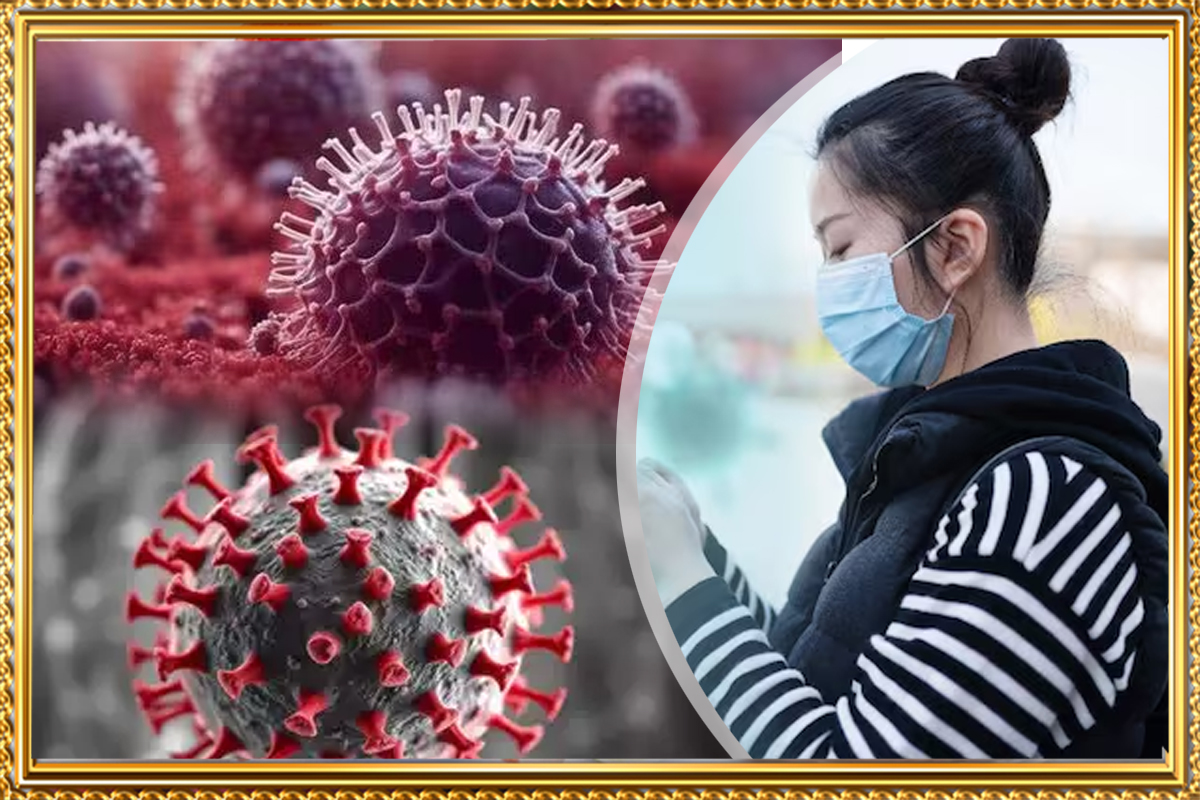
Explore the details of Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV), including symptoms, transmission, treatments, and comparisons with other respiratory viruses. Discover natural remedies, FAQs, and insights on the virus's impact on global health.
Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV) is a respiratory virus that primarily affects children, the elderly, and individuals with weakened immune systems. First identified in 2001, HMPV is a significant cause of respiratory infections worldwide. This article explores HMPV in depth, including symptoms, transmission, treatment options, and how it compares to other viruses like RSV and COVID-19. We'll also discuss whether HMPV poses a potential pandemic threat.
How is HMPV Transmitted?
What is HMPV?
Symptoms of HMPV
Difference Between HMPV and RSV
Treatments for HMPV
Could HMPV Cause a Pandemic?
Global and Regional Impacts
Positive Aspects of Home Remedies and Treatments
Negative Aspects of Home Remedies and Treatments
FAQs
CONCLUSION
How is HMPV Transmitted?
- Modes of Transmission: • Respiratory droplets from coughing or sneezing. • Direct contact with contaminated surfaces. • Close contact with infected individuals.
- Prevention Tips: • Practice good hygiene (frequent hand washing). • Use masks in crowded places. • Disinfect commonly touched surfaces.

What is HMPV?
- Definition: Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV) is a respiratory pathogen from the Paramyxoviridae family. It causes mild to severe respiratory illnesses, similar to influenza or RSV.
- Full Form: Human Metapneumovirus.
- Impact on the Body: HMPV primarily targets the respiratory system, leading to symptoms like cough, fever, and nasal congestion.
Symptoms of HMPV
- Common Symptoms: • Runny nose • Fever • Cough • Shortness of breath • Sore throat • Wheezing
- Symptoms in Babies: • Rapid breathing • Irritability • Difficulty feeding
- Potential Complications: • Bronchiolitis • Pneumonia • Exacerbation of asthma or COPD
Difference Between HMPV and RSV
- HMPV: • Affects all age groups, but severe cases are more common in children and the elderly. • Symptoms overlap with other respiratory viruses.
- RSV: • Primarily impacts infants and young children. • Often causes bronchiolitis and severe lower respiratory tract infections.
Treatments for HMPV
- Supportive Treatments: • Rest and hydration. • Over-the-counter medications to manage fever and pain. • Humidifiers to ease breathing.
- Antiviral Treatments: • Currently, no specific antiviral treatments are approved for HMPV. • Research is ongoing to develop effective therapies.
- Home Remedies: • Steam Inhalation: Helps relieve nasal congestion. • Honey and Ginger: Soothes the throat and reduces coughing. • Herbal Teas: Chamomile or green tea can boost immunity.
Could HMPV Cause a Pandemic?
- Current Status: HMPV is not considered as contagious or severe as COVID-19. It’s primarily a seasonal illness.
- Risk Assessment: • HMPV does not spread as rapidly as the coronavirus. • Health systems and protocols can manage its outbreaks effectively.
Global and Regional Impacts
- India: • Cases are rising in certain regions, including Bengaluru. • Infants and the elderly are the most affected groups.
- Health Authorities' Response: • Increased surveillance and awareness campaigns. • Guidelines for managing pediatric respiratory illnesses.
- Future Outlook: • Innovative Therapies: Development of combination antiviral drugs that target multiple respiratory viruses, including HMPV. • Integration into Respiratory Virus Panels: Routine screening for HMPV alongside influenza and RSV in clinical diagnostics. • Global Vaccination Strategies: Long-term plans to incorporate HMPV vaccines into childhood immunization schedules.
Environmental and Climatic Factors: • Air Pollution Link: Exposure to high levels of air pollutants may exacerbate HMPV symptoms and complications. • Climate Change Impact: Shifts in seasonal patterns may alter the typical timing and intensity of HMPV outbreaks.
- Emerging Research on HMPV: • Vaccination Development: Research into vaccines targeting HMPV is ongoing, with some promising candidates in preclinical trials. • Antiviral Innovations: Studies are exploring antiviral compounds, including monoclonal antibodies, that may offer targeted treatment for HMPV in the future. • Genomic Insights: Advances in genome sequencing of HMPV are helping researchers understand its evolution and potential mutations.
- Impact of HMPV on Healthcare Systems: • Burden on Pediatric Wards: HMPV outbreaks can lead to increased hospitalizations in children, especially during winter months. • Economic Implications: Costs associated with hospitalizations, treatments, and lost productivity during outbreaks. • Global Surveillance Needs: Strengthening diagnostic capabilities to differentiate HMPV from other respiratory viruses in clinical settings.
- Vulnerable Groups and Risk Factors: High-Risk Populations: • Immunocompromised individuals (e.g., cancer patients, organ transplant recipients). • Residents in long-term care facilities. • People with chronic respiratory diseases like asthma or COPD. • Seasonal Variations: Outbreaks are more common in late winter and early spring, emphasizing the need for seasonal preparedness.
- HMPV in the Post-COVID-19 Era: • Heightened Awareness: Public health focus on respiratory viruses post-pandemic has improved diagnostic and reporting capabilities. • Role of Masks and Social Distancing: Measures implemented for COVID-19 have shown ancillary benefits in reducing the spread of other respiratory viruses, including HMPV. • Cross-Virus Comparisons: The pandemic has provided insights into how different viruses spread, aiding in better HMPV management strategies.
- Diagnostic Tools and Challenges: Laboratory Diagnosis: • Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) is the gold standard for detecting HMPV. • Rapid antigen tests are being developed for quicker diagnosis. • Misdiagnosis Risks: Symptoms overlap with RSV, influenza, and COVID-19, potentially delaying specific care.
Positive Aspects of Home Remedies and Treatments
- Easily accessible and cost-effective.
- Fewer side effects compared to some medications.
- Supportive care enhances recovery.}
Negative Aspects of Home Remedies and Treatments
- May not address severe complications.
- Effectiveness varies from person to person.
- Lack of specific antiviral drugs for HMPV limits options.
FAQs
- Q1. Is HMPV more dangerous than COVID-19? A1. No, HMPV typically causes milder symptoms and is less contagious.
- Q2. How long has HMPV been known? A2. HMPV, first discovered in 2001, is believed to have been circulating for many decades before its identification.
- Q3. Are masks effective against HMPV? A3. Yes, masks help prevent the spread of respiratory droplets, reducing transmission.
- Q4. Can children recover from HMPV without hospitalization? A4. Most children recover at home with supportive care unless complications arise.
- Q5. How is HMPV similar to RSV? A5. Both cause respiratory infections with overlapping symptoms like wheezing and coughing.
Role of Nutrition and Lifestyle in Recovery: • Immune-Boosting Diet: Incorporating foods rich in vitamins C and D, zinc, and antioxidants supports recovery. • Hydration Importance: Staying hydrated helps thin mucus and reduces respiratory discomfort. • Rest and Sleep: Quality rest is crucial for immune system function and overall recovery.
Addressing Misconceptions About HMPV: • "It’s Just a Cold" Myth: While mild cases resemble a cold, severe infections can lead to hospitalization, particularly in vulnerable groups. • Antibiotics Misuse: Antibiotics are ineffective against viruses like HMPV and should not be used unless bacterial superinfection occurs.

Conclusion: HMPV is a common respiratory virus that requires awareness and prompt management, especially in vulnerable populations. While home remedies and supportive treatments are effective for mild cases, severe symptoms necessitate medical attention. By adopting preventive measures and understanding the nature of the virus, individuals can reduce the risk of infection and complications.











Post a comment