- Home
- What is H5N1 Bird Flu? Facts About the Virus in Birds and Humans
What is H5N1 Bird Flu? Facts About the Virus in Birds and Humans
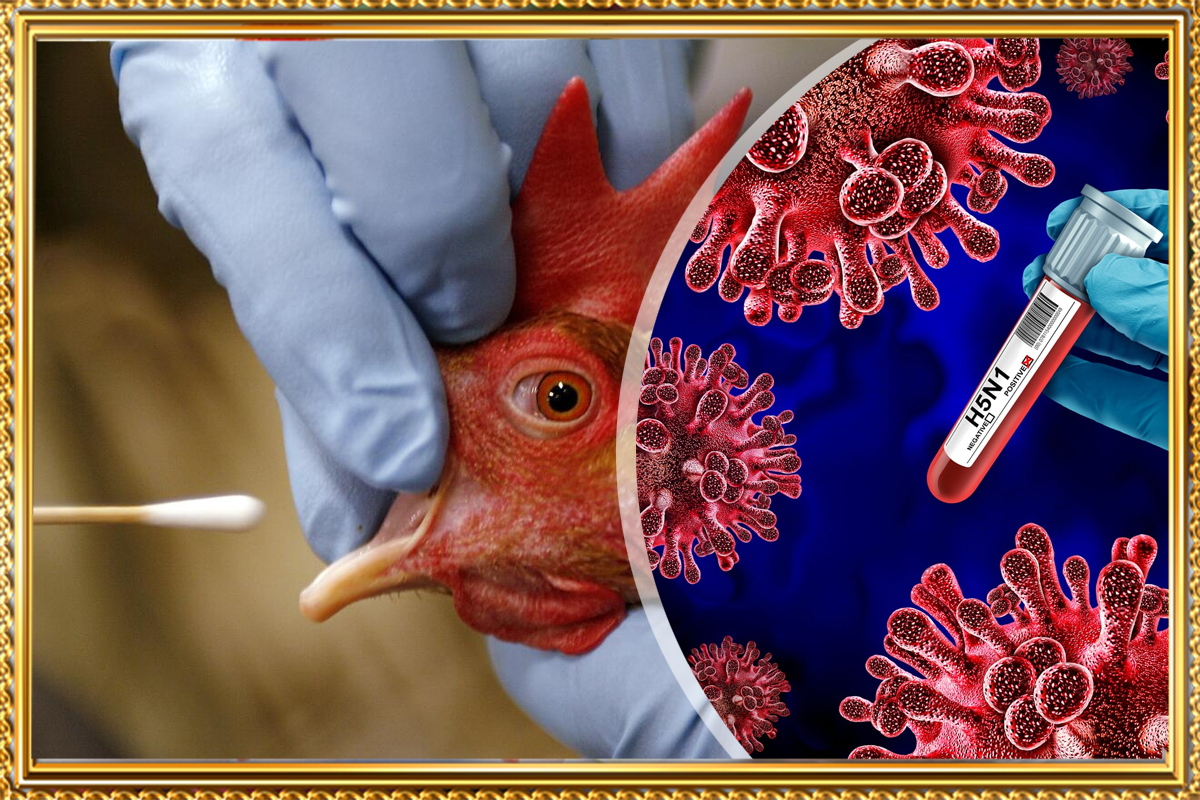
A comprehensive guide on the H5N1 bird flu, exploring its potential risks, human impact, preventive measures, and future outlook. Learn about its mutations, symptoms, and the possibility of a pandemic.
The H5N1 bird flu virus, also known as avian influenza, has raised global health concerns due to its potential to mutate and cause widespread outbreaks. While currently rare in humans, cases of animal-to-human transmission have been well-documented. This article delves into the current state of the H5N1 virus, its risks, and what we can do to prepare for a potential outbreak.
Recent Findings and Developments
Why is H5N1 a Concern?
Scientific Insights and Monitoring
Role of Governments and Organizations
Public Health Initiatives
Economic and Environmental Factors
Technological Innovations
Positive Aspects
Negative Aspects
FAQs
CONCLUSION
Recent Findings and Developments
- Mutation Identified in Human Cases: Recent studies have identified mutations in samples taken from infected patients. These mutations suggest the virus is evolving, though it has not yet gained the ability for sustained human-to-human transmission. Continuous monitoring is crucial.
- H5N1 Vaccines: Despite the low current risk to the general public, these vaccines could play a vital role in controlling future outbreaks.

Why is H5N1 a Concern?
- Potential for Mutation: One of the primary concerns with H5N1 is its ability to mutate. Scientists fear that the virus could acquire mutations enabling easier human-to-human transmission, leading to a pandemic.
- Documented Human Cases: While rare, human cases of H5N1 have been severe, with a high fatality rate. Most infections have occurred in people with close contact with infected birds or contaminated environments.
- Global Spread: The virus has been detected in birds across Asia, Europe, Africa, and North America, increasing the likelihood of cross-species transmission.
- What is H5N1 Bird Flu? First detected in humans in 1997, it has caused significant outbreaks in domestic poultry and occasional cases in humans who have close contact with infected birds. The virus is highly pathogenic in birds and can lead to severe respiratory symptoms and high mortality rates.
Scientific Insights and Monitoring
- Genomic Surveillance: Advances in genomic technology allow scientists to track mutations in real-time, providing early warnings about potential threats.
- Interdisciplinary Research: Collaboration between virologists, epidemiologists, and ecologists helps understand how the virus spreads across species and regions.
- Virus Evolution Models: Advanced computational models simulate how the virus may evolve, helping researchers anticipate future mutations.
- Zoonotic Research: Studies focus on understanding how H5N1 crosses species barriers, particularly from birds to humans.
Role of Governments and Organizations
- Policy Development: Governments are creating contingency plans, including stockpiling antivirals and drafting pandemic response strategies.
- World Health Organization (WHO): The WHO plays a critical role in coordinating global efforts, issuing guidelines, and facilitating vaccine distribution.
- International Trade Regulations: Governments are enforcing stricter guidelines on the trade of live poultry to prevent cross-border outbreaks.
- Funding for Research: Increased financial support for virology research accelerates the development of antiviral drugs and vaccines.
Public Health Initiatives
- Educational Campaigns: Targeted campaigns educate farmers, poultry workers, and the public about risks and safety practices.
- Rapid Response Teams: Many countries have developed rapid response units to contain outbreaks in poultry before they spread.
- Improved Surveillance Systems: Real-time data collection in high-risk areas ensures early detection of outbreaks.
- Vaccination Campaigns for Poultry: Large-scale vaccination efforts in domestic birds help control the spread of H5N1.
Economic and Environmental Factors
- Wildlife Conservation: Protecting wild bird habitats can reduce stress and limit the spread of diseases within bird populations.
- Sustainable Farming Practices: Encouraging biosecurity and humane poultry farming practices minimizes risks of outbreaks in domestic birds.
- Impact on Food Security: Outbreaks in poultry farming can lead to shortages and increased food prices globally.
- Climate Change Effects: Altered migratory patterns of birds due to climate change may spread the virus to new regions.
Technological Innovations
- AI and Big Data: Predictive models using AI and big data help identify high-risk areas for potential outbreaks.
- Innovative Vaccination Strategies: Novel approaches, such as DNA vaccines or vector-based vaccines, show promise in combating H5N1.
- Mobile Health Applications: Apps provide real-time updates and tips for individuals in outbreak-prone areas, increasing awareness and safety.
- Portable Testing Kits: Innovative testing devices enable rapid diagnosis of H5N1 in remote or rural locations.
- Societal Considerations: 1. Psychological Preparedness: Providing accurate information helps mitigate public fear and reduces stigma associated with avian influenza outbreaks. 2. Community Involvement: Local communities play a vital role in early detection and reporting of unusual bird deaths.
- Lessons from Past Pandemics: 1. Swift Action is Crucial: The COVID-19 pandemic highlights the importance of rapid, coordinated action to contain infectious diseases. 2. Strengthening Healthcare Systems: Investing in healthcare infrastructure ensures readiness for potential pandemics, including avian flu.
- Future Outlook: 1. Global Vaccine Development Pipeline: The global push for universal influenza vaccines may provide long-term solutions for managing all flu strains, including H5N1. 2. One Health Approach: Integrating human, animal, and environmental health strategies is key to tackling zoonotic diseases like H5N1.
Positive Aspects
- Advances in Vaccine Development: Ongoing research has made significant progress in creating effective vaccines against H5N1.
- Increased Awareness: Public health initiatives and media coverage have improved awareness about bird flu and preventive measures.
- Global Cooperation: Countries are working together to monitor outbreaks, share data, and control the spread of the virus.}
Negative Aspects
- High Fatality Rate: Human infections have resulted in severe illness and high mortality, raising alarm among health professionals.
- Economic Impact: Outbreaks in poultry can devastate the farming industry, leading to financial losses and food supply disruptions.
- Pandemic Potential: If the virus mutates to enable easier human-to-human transmission, the consequences could be catastrophic.
FAQs
- What are the symptoms of H5N1 in humans? Common symptoms include high fever, cough, difficulty breathing, and severe respiratory distress. In critical cases, it may progress to pneumonia, organ dysfunction, and can be life-threatening.
- Can over-the-counter medications treat H5N1? No, H5N1 requires antiviral medications like oseltamivir or zanamivir. Over-the-counter drugs may alleviate symptoms but do not treat the virus itself.
- Why hasn’t H5N1 caused large-scale human outbreaks? The virus has not yet developed the ability to spread efficiently between humans, limiting its outbreak potential.
- Is it possible to eradicate H5N1? Complete eradication is challenging due to its presence in wild bird populations. However, controlling its spread in domestic birds is achievable through vaccination and biosecurity measures.
- What can individuals do to prevent infection? Avoid direct contact with birds, practice good hygiene, and stay informed about outbreaks in your area.
Conclusion

The H5N1 bird flu remains a significant concern due to its potential to cause severe outbreaks and economic disruption. While the current risk to the general public is low, vigilance, research, and preparedness are essential to mitigate its impact. By understanding the virus and supporting public health initiatives, we can reduce the threat it poses and ensure a safer future.










Post a comment