- Home
- HMPV Virus Explained: How It Spreads and How to Protect Yourself
HMPV Virus Explained: How It Spreads and How to Protect Yourself
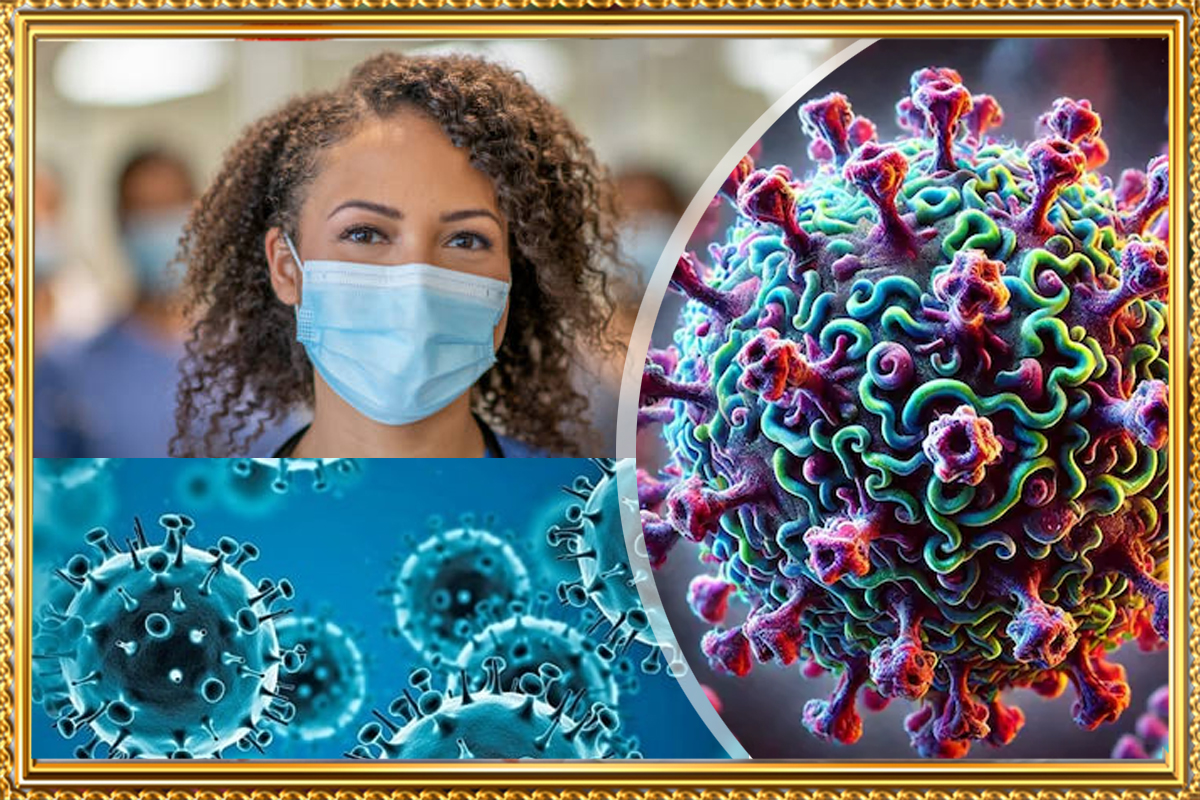
Discover all about Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV), its symptoms, transmission methods, prevention strategies, and its impact on global health. Learn how to stay safe and informed.
Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV) is an important respiratory virus affecting individuals of all ages, with children, elderly, and immunocompromised individuals being at higher risk. Despite its prevalence, HMPV remains relatively unknown compared to other respiratory illnesses like the flu or RSV. This article delves into HMPV's symptoms, how it spreads, ways to prevent it, and its broader implications.
How Does HMPV Spread?
Symptoms of HMPV
Prevention Strategies
Symptoms
Transmission
Prevention Strategies
Emerging Research Areas
Impact on Public Health
Positive Aspects of HMPV Awareness
Negative Aspects of HMPV
FAQs
CONCLUSION
How Does HMPV Spread?
HMPV spreads through:
- Respiratory Droplets: The virus spreads through droplets released into the air when an infected person coughs or sneezes.
- Direct Contact: Touching someone who is infected.
- Contaminated Surfaces: The virus can survive on surfaces for a limited time. Infection can occur by touching a contaminated surface and then touching your face, especially your eyes, nose, or mouth.

Symptoms of HMPV
Common symptoms include:
- Mild cases: Common symptoms include a runny nose, sore throat, cough, and fever.
- Severe cases: Wheezing, difficulty breathing, and signs of bronchitis or pneumonia.
- High-risk groups (infants, elderly, and immunocompromised individuals) are more likely to experience severe symptoms.
- What is Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV)? Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV), a respiratory virus, was first discovered in 2001. It is part of the Paramyxoviridae family and is closely related to Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV). It commonly causes respiratory infections ranging from mild cold-like symptoms to severe conditions like bronchitis and pneumonia.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing the spread of HMPV involves:
- Hand Hygiene: Regular hand washing with soap and water.
- Use of Masks: Masks can help reduce the spread of respiratory droplets.
- Avoiding Close Contact: Stay away from infected individuals.
- Disinfecting Surfaces: Clean commonly touched surfaces frequently.
- Boosting Immunity: A healthy diet, exercise, and adequate sleep can strengthen the immune system.
Symptoms
- Asymptomatic Cases: Some individuals, particularly healthy adults, may carry and spread the virus without showing symptoms.
- Long-term Effects: Repeated infections can occur, and in some cases, prolonged illness or complications may arise, particularly in vulnerable groups.
- Symptoms in Immunocompromised Individuals: People with weakened immune systems (e.g., cancer patients, transplant recipients) can develop more severe or prolonged symptoms such as acute respiratory failure or pneumonia.
- Mild Illness in Healthy Adults: While adults often experience mild cold-like symptoms, in rare cases, HMPV can lead to more serious conditions like severe bronchiolitis, particularly in previously healthy individuals.
Transmission
- Airborne Transmission: Although primarily spread through droplets, recent studies suggest that HMPV may also be transmitted through aerosols in poorly ventilated areas, increasing the need for effective air filtration systems in hospitals and schools.
- Crowded Environments: Close-quarters settings, such as daycares, schools, and nursing homes, present higher risks for HMPV outbreaks due to prolonged exposure to respiratory droplets.
- Environmental Persistence: HMPV can persist on surfaces for several hours to days, especially in cold and dry conditions, which makes cleaning and disinfection critical in high-risk areas.
- Seasonality: HMPV infections often peak in late winter and spring, similar to other respiratory viruses.
- Viral Shedding Duration: Immunocompromised individuals may shed the virus for longer periods, increasing transmission risks.
Prevention Strategies
Protecting High-Risk Groups: During peak seasons, special attention should be given to protecting high-risk individuals, such as those in long-term care facilities, by reducing exposure to the virus.
- Vaccination Research: Although there’s no vaccine yet, ongoing research focuses on developing immunizations for at-risk groups.
- Public Health Campaigns: Increased education on respiratory hygiene can help mitigate spread in schools, workplaces, and public spaces.
- Role of Ventilation: Ensuring proper ventilation in indoor spaces can reduce the risk of airborne transmission.
- Educational Initiatives: Public health campaigns that educate people on HMPV transmission and prevention strategies can significantly reduce its spread, especially in schools and daycare centers.
- Immunity Through Infection: Some individuals who get infected with HMPV may develop partial immunity, which could protect them from reinfection in the future. However, immunity tends to wane over time, and reinfections can occur. Disinfection Guidelines: Emphasizing the importance of frequent cleaning and disinfecting surfaces, especially in public places and healthcare facilities, to reduce the chances of indirect transmission.
Emerging Research Areas
- Genetic Variability of HMPV: Studies on different strains of the virus can provide insights into its spread and severity.
- Long-Term Immunity: Research is ongoing to understand the duration and effectiveness of immunity following HMPV infection.
- Antiviral Development: Efforts to develop broad-spectrum antivirals that target paramyxoviruses, including HMPV, are gaining traction.
Impact on Public Health
- Pediatric Burden: HMPV is a leading cause of hospitalizations in children for lower respiratory tract infections.
- Healthcare Policy Implications: Awareness of HMPV can inform vaccination strategies and pandemic preparedness frameworks for respiratory viruses.
Positive Aspects of HMPV Awareness
- Global Focus: Increased awareness can lead to better hygiene practices and public health measures.
- Research Opportunities: Highlighting HMPV's impact encourages research into vaccines and treatments.
- Community Health Improvements: Preventive measures for HMPV can also help control other respiratory illnesses.}
- Improved Surveillance: Enhanced monitoring of HMPV can lead to better outbreak prediction and control measures.
- Collaborative Efforts: Awareness encourages global collaboration among researchers, healthcare providers, and policymakers to address respiratory illnesses.
Negative Aspects of HMPV
- Lack of Specific Treatments: The absence of targeted antivirals or a vaccine limits treatment options.
- Impact on Healthcare Systems: Outbreaks can overwhelm healthcare facilities, especially during peak respiratory illness seasons.
- Economic Burden: Severe cases require hospitalization, leading to increased healthcare costs.
- Misdiagnosis Risks: Symptoms of HMPV overlap with other respiratory illnesses, leading to potential misdiagnoses or delayed treatments.
- Inequities in Healthcare Access: Vulnerable populations, particularly in low-income regions, may face greater challenges in accessing supportive care.
FAQs
Can HMPV co-infect with other viruses? Yes, co-infections with viruses like influenza or RSV are common and can worsen respiratory symptoms.
- Can HMPV cause severe respiratory conditions? Yes, in high-risk groups, HMPV can lead to bronchitis, pneumonia, or even acute respiratory distress.
- Is there a vaccine for HMPV? No, there is currently no vaccine or specific antiviral treatment for HMPV. Managing symptoms primarily involves supportive care, such as rest, hydration, and over-the-counter medications.
- How long is HMPV contagious? Individuals infected with HMPV can spread the virus for several days, even if symptoms are mild.
- Can masks help prevent HMPV spread? Yes, wearing masks can reduce the transmission of respiratory droplets, which are the primary mode of spread for HMPV.
- Are children more susceptible to HMPV? Yes, children under five years are particularly vulnerable, often experiencing more severe symptoms compared to adults.
Conclusion

HMPV is a significant yet underrecognized respiratory virus that requires more public attention and research. Preventive measures like proper hygiene, wearing masks, and avoiding contact with infected individuals are vital to controlling its spread. While the lack of a vaccine or specific antiviral therapy remains a challenge, increased awareness and global health initiatives can pave the way for better management and future breakthroughs.










Post a comment